Trees
- There is different types of trees such as
Binary Trees,Binary Search Trees, andK-ary Trees.
Common Terminology
- Node - A Tree node is a component which may contain it’s own values, and references to other nodes
- Root - The root is the node at the beginning of the tree
- K - A number that specifies the
maximum numberof children any node may have in ak-ary tree. In abinary tree, k = 2. - Left - A reference to
one child node, in abinary tree - Right - A reference to the
other child node, in abinary tree - Edge - The edge in a tree is the link between a parent and child node
- Leaf - A leaf is a node that does not have any children
- Height - The height of a tree is the number of edges from the root to the furthest leaf
Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree can have any number of children per node, but Binary Trees restrict the number of children to two (hence our left and right children).
-
There is no specific sorting order for a binary tree. Nodes can be added into a binary tree wherever space allows.
Traversals for binary trees
- An important aspect of trees is how to traverse them. Traversing a tree allows us to search for a node, print out the contents of a tree, and much more!
-
There are two categories of traversals when it comes to trees:
- Depth First
- Breadth First
Depth First
- Depth first traversal is where we prioritize going through the depth (height) of the tree first.there are multiple ways to carry out depth first traversal, and each method changes the order in which we search/print the root.
- Here are three methods for depth first traversal:
- Pre-order: root » left » right
- In-order: left » root » right
- Post-order: left » right » root
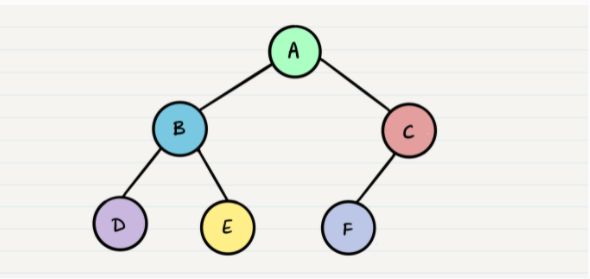
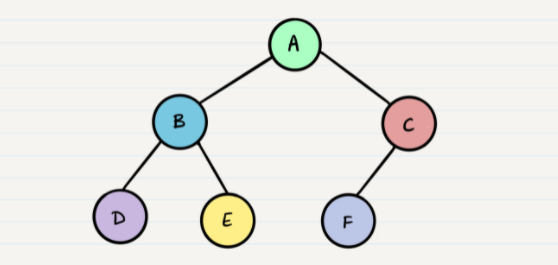
Example:
-
If we have this sample of tree , the traversals would result in different paths:
- Pre-order:
A, B, D, E, C, F - In-order:
D, B, E, A, F, C - Post-order:
D, E, B, F, C, A
- Pre-order:
-
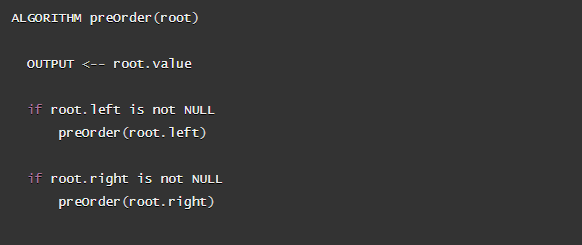
Pre-order
-
Pre-order means that the
roothas to be looked atfirst. When we call preOrder for the first time, therootwill be added to the call stack. we start reading our preOrder function’s code from top to bottom. This means that we will output the root.value out to the console.And it will start check the left of the root then when it’s finished it will check the right of the root.
When the root.left and root.right will return null the next node will act as the root to continue execution
Here is the pseudocode for this traversal method:
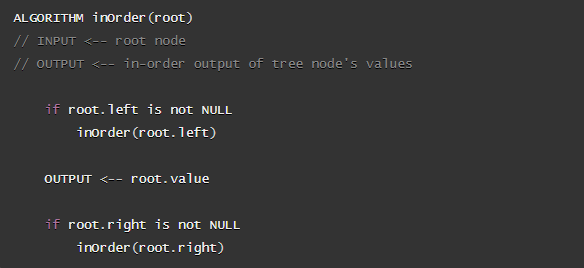
- In-order
Here is the pseudocode for this traversal method:
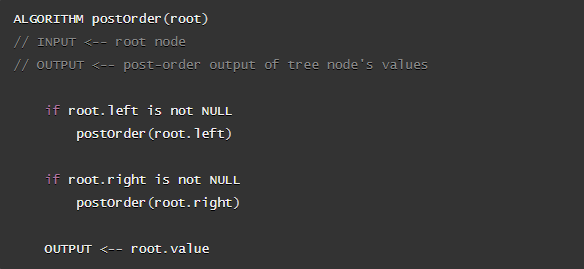
- post-order
Here is the pseudocode for this traversal method:
The previous tree traversals are similar but the difference between each of the traversals is when you are looking at the
root node.
Breadth First
- Breadth first traversal iterates through the tree by going through each level of the tree
node-by-node. breadth first traversal uses a queue
Example:
- Our output using breadth first traversal is now:
Output: A, B, C, D, E, F
- It will start with
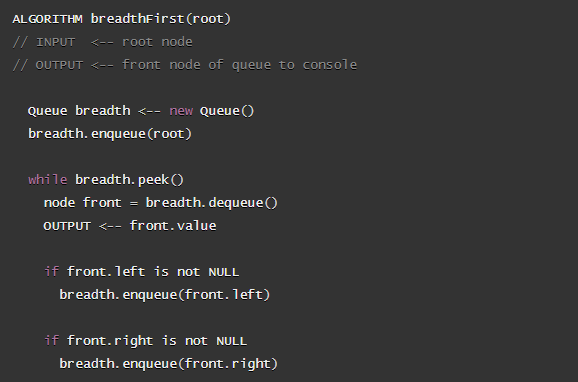
addingthe root to thequeueto fill it the it willdequeuethe root and startenqueuethe left and right child in that order. thendequeue the front node,enqueuethat node’sleftandrightnodes, and move to the next new front of the queue. And so on until we reach a node that doesn’t have any children, we just dequeue it without any further enqueue.
Here is the pseudocode, utilizing a built-in queue to implement a breadth first traversal.
K-ary Trees
- If Nodes are able have more than
2 child nodes, we call the tree that contains them aK-ary Tree. In this type of tree we useKto refer to themaximum number of childrenthat each Node is able to have.
Traversals for K-ary trees
Breadth First Traversal
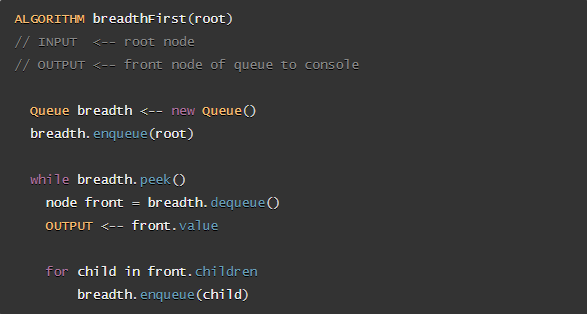
- We are still pushing nodes into a
queue, but we are now moving down a list of children oflength k, instead of checking for the presence of aleft and a right child.
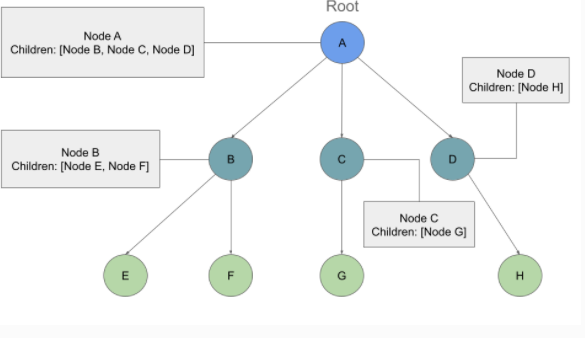
Example:
- If we traversed this tree Breadth First we should see the output:
Output: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
- We will start by adding the
rootto thequeue,then we willdequeueit and now we will startenqueue the childerof the root ,then we will check thefrontanddequeueit andenqueue it's children, followed by enqueing the current Node’s children continues until our queue isempty of child Nodes.
Here is the pseudocode
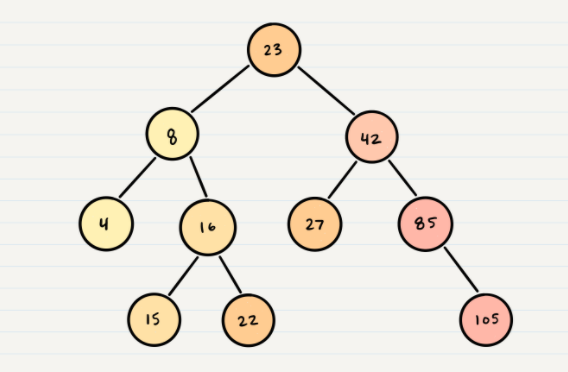
Binary Search Trees
Binary Search Tree (BST)is a type of tree that does have some structure attached to it. In a BST, nodes are organized in a manner where all values that aresmaller than the rootare placed to theleft, and all values that arelarger than the rootare placed to theright.
Example:
- The best way to approach a BST search is with a while loop. We cycle through the while loop until we hit a leaf, or until we reach a match with what we’re searching for.
References:
@By codefellows/Trees